20 Marketing Terms
You Need To Know
You’ve just stepped foot in the marketing world and soon find yourself constantly surrounded by industry jargon. If you don’t know the exact meaning of these marketing terms, you will likely have a rather challenging time trying to catch up with all the latest marketing trends and news.
So, to help you along the way, I’ve decided to pull together some important marketing terms that every new marketer needs to know. Whether you are reading about the newest marketing trend, planning a marketing strategy, or analyzing brands and campaigns, you will likely see or hear these terms wherever you go.
TOPICS TO COVER
IMPORTANT MARKETING TERMS YOU NEED TO KNOW
-
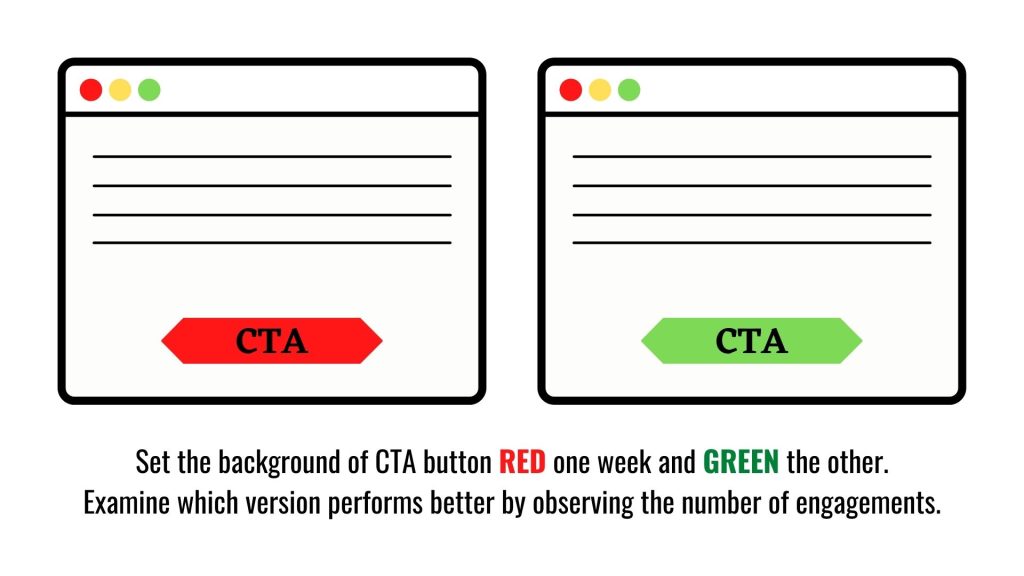
A/B Testing
A/B Testing is a kind of marketing experiment that examines the effectiveness of elements—the color of a button, the placement of an image, the number of navigation links, etc.
It aims to understand what users (humans) prefer by comparing two sets of elements and determining which version performs better.
-
Analytics
In simple terms. analytics is used to discover and identify patterns (trends), helping users to discover interesting and meaningful things that they might have missed.
It is done by tracking, gathering, interpreting, and analyzing a set of data. Marketers will then make use of the results obtained to make better marketing decisions.
-
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate tells how visitors feel and engage with a website’s content. It is calculated based on the percentage of people visiting a page, then left without taking any actions (continue viewing other pages within the same website).
Your aim is to get a lower bounce rate. If your bounce rate is low, it means that your visitors are spending more time and are engaging with other content within your website.
-
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Call-to-Action (CTA) refers to any designs that serve as an invitation for visitors to take the desired action. It could be a button, an image, a navigation link, or text messages that tell audiences what they should be doing.
-
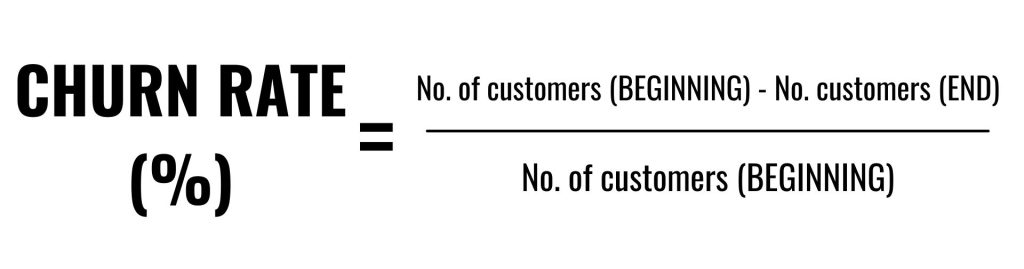
Churn Rate
Churn rate is more commonly used by subscription-based businesses/companies. It is a metric that tells a company how many customers they have lost over a given period of time.
-
Clickthrough Rate (CTR)
Clickthrough rate is commonly used to measure the success of a marketing campaign. It is the ratio of visitors who engage with a specific element (often a link) to the number of times the element has been exposed to people.
-
Conversion Rate (CR)
Conversion rate calculates the percentage of website visitors who have taken and completed the desired action. It is calculated by taking the number of visitors who completed the conversion, versus the total number of visitors.
-
Earned Media
Earned media, sometimes also known as earned content or free media, is a type of media/coverage/publicity that is generated and gained without paying anyone to do so. In other words, you can see it as online word-of-mouth.
The most effective way to gain earned media is a combination of organic search rankings and great content.
- High-rank content = More visibility
(Best if it’s on the first page of search engine results pages) - Good content = More engagement
(More likely to be commented, shared, reposted, recommended, picked up by others, etc.)
-
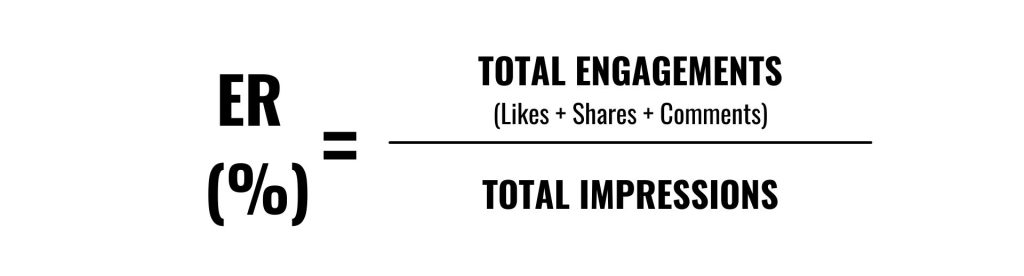
Engagement Rate (ER)
Engagement rates aim to understand how your audiences are interacting with your social media content. It measures the number of likes, shares, and comments your content receives.
-
Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
Key performance indicator (KPI) is used to evaluate and understand how a company is performing. It is a metric that tracks a company’s progress towards achieving a set of business goals.
-
Keywords
Keywords, in SEO terms, are words and phrases that people are entering into search engines. Content-wise, these are terms that define what your content is about.
If you want to increase the chances of people finding your content, you will have to tailor your content and include relevant keywords to what internet users are searching for.
-
Marketing Page
Marketing page, sometimes known as a landing page, refers to a kind of web page designed with a specific goal in mind. It is a standalone web page that aims to persuade visitors (your potential customers) to provide personal details in exchange for something valuable.
Depending on the goal of the marketing page, it can also be called a “click-through page”, “infomercial page”, “lead capture page”.
-
Organic traffic
Organic traffic visits that are coming directly from searches on search engines. These are “free” traffic that comes from organic search results—ranked by popularity and relevance—rather than through paid advertisements.
-
Owned Media
Owned media refers to any media channels/platforms that a company owns and has total control of. These are your digital properties such as company websites and any social media channels.
-
Paid Media
In simple words, paid media refers to any marketing that you are paying for to promote your content on any external platforms. Examples include paying influencers to represent and promote your products, paid media advertisements on social media, display ads on external websites, etc.
-
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on investment is a kind of profitability metric that evaluates the profitability—the revenue growth—of an investment. It is calculated by comparing how much a company has earned from investment to how much they have paid for.
However, it is to note that ROI usually does not take into account a lot of different costs such as hidden costs, duration of projects, inflation, time value of money, etc.
-
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Search engine marketing makes use of paid strategies to increase a website’s visibility on SERPs. Also known as pay-per-click (PPC), SEM is done via paid advertising, by buying up ad spaces on search engines like Google.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Unlike SEM, search engine optimization (SEO) focuses on refining and improving a website’s content and structure to increase its organic traffic. These are “free” website traffic that comes directly from visitors.
I’ve quoted “free” because while it is true that you don’t need to pay anything extra to get a higher search ranking and website traffic. You have to put a lot of time and effort into optimizing your website before you can see positive results.
Social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok are additional media channels used to achieve and serve different marketing purposes.
You can use it as a digital product to reach out to a wider audience, improve a website’s SEO like building backlinks), an additional channel to promote your product and increase sales, an easier and more effective way to connect with potential customers, and more.
-
Target Audience
Target audience refers to a specific group of people who are likely to be interested in your product or services. You can identify them by a myriad of characteristics such as age, gender, income level, interests, occupation, marital status, and more.
When creating marketing materials or any media content, it is important to cater your content to the said audiences. After all, these are the ones who are most likely to bring you business.
Two other important terms that you should know (that aren’t marketing terms):
Content Management System (CMS)—E.g. WordPress
CMS is a full-blown website-building solution that offers more flexibility for users to customize their websites.
While users can have full control over their website, this often requires some level of technical expertise and understanding of coding languages.
Website Builders—E.g. Website.com
Website building solution built with simplicity and ease-of-use in mind. Ideal solution for people who do not have any knowledge in website building.
The major downside is that website builders are much less customizable compared to CMS platforms. Users are more or less stuck with the features that a specific service provider is offering, though still powerful enough for the majority of small businesses.



Social Media